The Restaurant Point of sales System is developed using python. The project is built to manage items and transactions. To make a new transaction, fields such as: Item and ingredients , qty and payment needs to be selected. If you like to learn point of sales systems step by step, this is the right place to learn from the beginning.
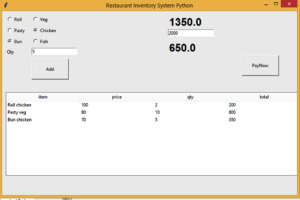
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
def pay():
totall = float(tot.cget("text"))
pay = float(e11.get())
bal = pay - totall
balText.set(bal)
def selection():
selection = radio.get()
selection1 = radio1.get()
qty = int(e1.get())
if(selection==1):
if(selection1 ==1):
item = "Roll"
inge = "veg"
price = 50
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge , price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection1 == 2):
item = "Roll"
inge = "chicken"
price = 100
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection1 == 3):
item = "Roll"
inge = "Fish"
price = 80
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection == 2):
if (selection1 == 1):
item = "Pasty"
inge = "veg"
price = 80
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection1 == 2):
item = "Pasty"
inge = "chicken"
price = 90
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection1 == 3):
item = "Pasty"
inge = "Fish"
price = 120
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection == 3):
if (selection1 == 1):
item = "Bun"
inge = "veg"
price = 60
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection1 == 2):
item = "Bun"
inge = "chicken"
price = 70
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
elif (selection1 == 3):
item = "Bun"
inge = "Fish"
price = 40
tot = int(price * qty)
tempList = [[item + " " + inge, price, qty, tot]]
tempList.sort(key=lambda e: e[1], reverse=True)
for i, (item, price, qty, tot) in enumerate(tempList, start=1):
listBox.insert("", "end", values=(item, price, qty, tot))
sum1 = 0.0
for child in listBox.get_children():
sum1 += float(listBox.item(child, 'values')[3])
totText.set(sum1)
top = Tk()
top.geometry("800x500")
top.title("Restaurant Inventory System Python")
radio = IntVar()
radio1 = IntVar()
global totText
global balText
totText = StringVar()
balText = IntVar()
R1 = Radiobutton(top, text="Roll", variable=radio, value=1)
R1.pack(anchor=W)
R1.place(x=10,y=10)
R2 = Radiobutton(top, text="Pasty", variable=radio, value=2)
R2.pack(anchor=W)
R2.place(x=10,y=40)
R3 = Radiobutton(top, text="Bun", variable=radio, value=3)
R3.pack(anchor=W)
R3.place(x=10,y=70)
R4 = Radiobutton(top, text="Veg", variable=radio1, value=1)
R4.pack(anchor=W)
R4.place(x=80,y=10)
R2 = Radiobutton(top, text="Chicken", variable=radio1, value=2)
R2.pack(anchor=W)
R2.place(x=80,y=40)
R3 = Radiobutton(top, text="Fish", variable=radio1, value=3)
R3.pack(anchor=W)
R3.place(x=80,y=70)
e1 = Entry(top)
e1.place(x=80, y=100)
Label(top, text="Qty").place(x=10, y=100)
tot = Label(top, text="",font="arial 22 bold", textvariable=totText)
tot.place(x=450, y=10)
Button(top, text="Add",command = selection,height=3, width= 13).place(x=80, y=130)
e11 = Entry(top)
e11.place(x=450, y=50)
e12 = Entry(top)
balance = Label(top, text="",font="arial 22 bold", textvariable=balText).place(x=450, y=80)
Button(top, text="PayNow",command = pay,height=3, width= 13).place(x=650, y=120)
cols = ('item', 'price', 'qty','total')
listBox = ttk.Treeview(top, columns=cols, show='headings')
for col in cols:
listBox.heading(col, text=col)
listBox.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=2)
listBox.place(x=10, y=220)
top.mainloop()
