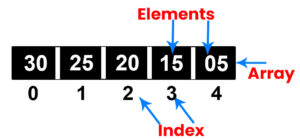


Array Index always start with 0 position.
Example 1
public class Ex1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numbers[];
numbers = new int[6];
numbers[0] = 30;
numbers[1] = 25;
numbers[2] = 20;
numbers[3] = 15;
numbers[4] = 5;
for(int x=0; x<5; x++)
{
System.out.println("Numbers " +(x+1) + " is " + numbers[x]) ;
}
}
}Output
Numbers 1 is 30
Numbers 2 is 25
Numbers 3 is 20
Numbers 4 is 15
Numbers 5 is 5
Example 2
public class Ex2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int groups[];
groups = new int[10];
groups[0] = 30;
groups[1] = 25;
groups[2] = 20;
groups[3] = 15;
groups[4] = 5;
groups[5] = 23;
groups[6] = 48;
for(int a=0; a<7; a++)
{
System.out.println("Group " +(a+1)+ "=" + groups[a]);
}
}
}Output
Group 1=30
Group 2=25
Group 3=20
Group 4=15
Group 5=5
Group 6=23
Group 7=48
Example 3
public class Ex3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String names[];
names = new String[4];
names = new String[4];
names[0] = "John";
names[1] = "James";
names[2] = "Steve";
names[3] = "Hume";
for(int x=0; x<4; x++)
{
System.out.println(names[x]);
}
}
}
Output
John
James
Steve
Hume
Example 4
public class Ex4{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String names[] = {"John","James","Jap","Sam"};
for(int x=0; x<4; x++)
{
System.out.println(names[x]);
}
}
}Example 5
public class Ex5{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int groups[] = {10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100};
for(int x=0; x<10; x++)
{
System.out.println(groups[x]);
}
}
}Output
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Example 6
public class Ex6{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String names[] = {"John","Jim","Peter","Anne","James"};
int ages[] ={15,20,23,21,28};
for(int x=0; x<5; x++)
{
System.out.println(names[x] + " is " + ages[x] + " Years Old" );
}
}
}Output
John is 15 Years Old
Jim is 20 Years Old
Peter is 23 Years Old
Anne is 21 Years Old
James is 28 Years Old
Two Dimensional Arrays
Example 1
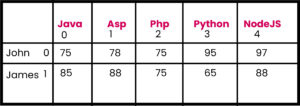


public class Ex1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String names[] = {"John","James"};
String courses[] = {"Java","Asp","Php","Python","NodeJS"};
int marks[][] = new int[2][5];
marks[0][0]=75;
marks[0][1]=78;
marks[0][2]=75;
marks[0][3]=95;
marks[0][4]=97;
marks[1][0]=85;
marks[1][1]=88;
marks[1][2]=75;
marks[1][3]=65;
marks[1][4]=88;
System.out.println("John");
for(int row=0; row<1; row++)
for(int col=0; col<5; col++)
System.out.println(courses[col]+ "=" + marks[row][col]);
System.out.println("_________________________________");
System.out.println("James");
for(int row=1; row<2; row++)
for(int col=0; col<5; col++)
System.out.println(courses[col]+ "=" + marks[row][col]);
}Output
John
Java=75
Asp=78
Php=75
Python=95
NodeJS=97
_________________________________
James
Java=85
Asp=88
Php=75
Python=65
NodeJS=88
Example 2
public class Ex2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String names[] = {"John","James"};
String courses[] = {"Java","Asp","Php","Python","NodeJS"};
int marks[][] = {{75,78,75,95,97},{85,88,75,65,88}};
System.out.println("John");
for(int row=0; row<1; row++)
for(int col=0; col<5; col++)
System.out.println(courses[col]+ "=" + marks[row][col] );
System.out.println("_________________________");
System.out.println("James");
for(int row=1;row<2;row++)
for(int col=0; col<5; col++)
System.out.println(courses[col]+ "=" + marks[row][col]);
}
}Example 3
public class Ex3{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int students[]={10,20,30,40};
System.out.println("Number of classes= " +students.length);
}
}Example 4
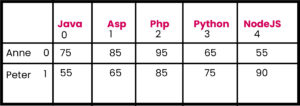


public class Ex4{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String exams[] = {"Anne","Peter"};
String courses[]={"Java","Asp","Php","Python","NodeJS"};
int marks[][]={{75,85,95,65,55},{55,65,85,75,90}};
System.out.println("Anne");
for(int row=0; row<1; row++)
for(int col=0; col<1; col++)
System.out.println(courses[col]+ " =" + marks[row][col]);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
System.out.println("Peter");
for(int row=1; row<2; row++)
for(int col=0; col<5; col++)
System.out.println(courses[col]+ " =" + marks[row][col]);
System.out.println("Number of Subject " + marks[0].length);
System.out.println("Number of Names " + marks.length);
}
}Output
Anne
Java =75
———————————–
Peter
Java =55
Asp =65
Php =85
Python =75
NodeJS =90
Number of Subject 5
Number of Names 2
Example 5
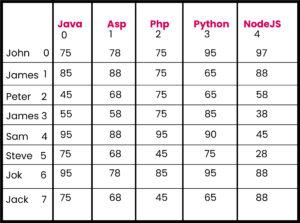


public class Ex5{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String courses[] = {"Java","Asp","Php","Python","NodeJS"};
String Student[] = {"John","James","Peter","James","Sam","Steve","Jok","Jack"};
int Marks[][] ={{75,78,75,95,97},{85,88,75,65,88},{45,68,75,65,58},
{55,58,75,85,38}, {95,88,95,90,45},{75,68,45,75,28},{95,78,85,95,88},
{75,68,45,65,88}};
System.out.println("Number of Students = " + Marks.length);
System.out.println("Number of Courses = " + Marks[0].length);
}
}Output
Number of Students = 8
Number of Courses = 5
import java.util.*;
class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] number = new int[5];
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++){
System.out.print("Enter Number " + (i + 1) + " : ");
number[i] = input.nextInt();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("All Numbers : [ ");
for(int i = 0 ; i < number.length ; i++){
System.out.print(number[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
Output
Enter Number 1 : 56
Enter Number 2 : 78
Enter Number 3 : 45
Enter Number 4 : 67
Enter Number 5 : 89
All Numbers : [ 56 78 45 67 89 ]
import java.util.*;
class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.print("Do you want to add new Student.? (Y/N) : ");
String letter = input.next();
System.out.println();
switch(letter){
case "Y":
System.out.print("Enter Student Name : ");
String name = input.next();
System.out.print("Enter Student Address : ");
String address = input.next();
System.out.print("Enter Number of Subjects : ");
int number_of_subjects = input.nextInt();
System.out.println();
int[] marks = new int[number_of_subjects];
int max = 0;
int total = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < number_of_subjects ;){
System.out.print("Enter Subject " + (i + 1) + " Marks : ");
marks[i] = input.nextInt();
if(marks[i] > 100){
System.out.println("Marks is Grater than 100.");
System.out.println();
continue;
}
if(max < marks[i]){
max = marks[i];
}
total = total + marks[i];
i++;
}
boolean flag = true;
while(flag){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("A. Show Student Details.");
System.out.println("B. Show All Marks.");
System.out.println("C. Show Maximum Marks.");
System.out.println("D. Show Total,Average & Result.");
System.out.println("X. Exit.");
System.out.println();
System.out.print("Please select one option : ");
letter = input.next();
System.out.println();
switch(letter){
case "A":
System.out.println("Student Name : " + name);
System.out.println("Student Address : " + address);
break;
case "B":
for(int i = 0 ; i < marks.length ; i++){
System.out.println("Subject " + (i + 1) + " Marks : " + marks[i]);
}
break;
case "C":
System.out.println("Maximum marks : " + max);
break;
case "D":
double average = (double)total / number_of_subjects;
String result = "pass";
if(average < 50){
result = "Fail";
}
System.out.println("Total : " + total);
System.out.println("Average : " + average);
System.out.println("Result : " + result);
break;
case "X":
System.out.println("Have a nice day..!");
flag = false;
break;
default :
System.out.println("Please select valid option..");
}
}
break;
case "N":
System.out.println("Good bye....");
return;
default :
System.out.println("Please enter valid letter..");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output
Do you want to add new Student.? (Y/N) : Y
Enter Student Name : John
Enter Student Address : India
Enter Number of Subjects : 3
Enter Subject 1 Marks : 78
Enter Subject 2 Marks : 89
Enter Subject 3 Marks : 54
A. Show Student Details.
B. Show All Marks.
C. Show Maximum Marks.
D. Show Total,Average & Result.
X. Exit.
Please select one option : A
Student Name : John
Student Address : India
A. Show Student Details.
B. Show All Marks.
C. Show Maximum Marks.
D. Show Total,Average & Result.
X. Exit.
Please select one option : A